Upper Back Stretches: The Three Must Do Exercises To Improve Your Thoracic Spine Mobility
Do you spend most of your day sitting at a desk, or hunched over your phone or computer? This hunched-over posture is super common, and often leads to developing upper back pain.
If you suffer from a stiff thoracic spine, here are three upper back stretches to help you open up through your upper back.
How do you stretch your upper back?
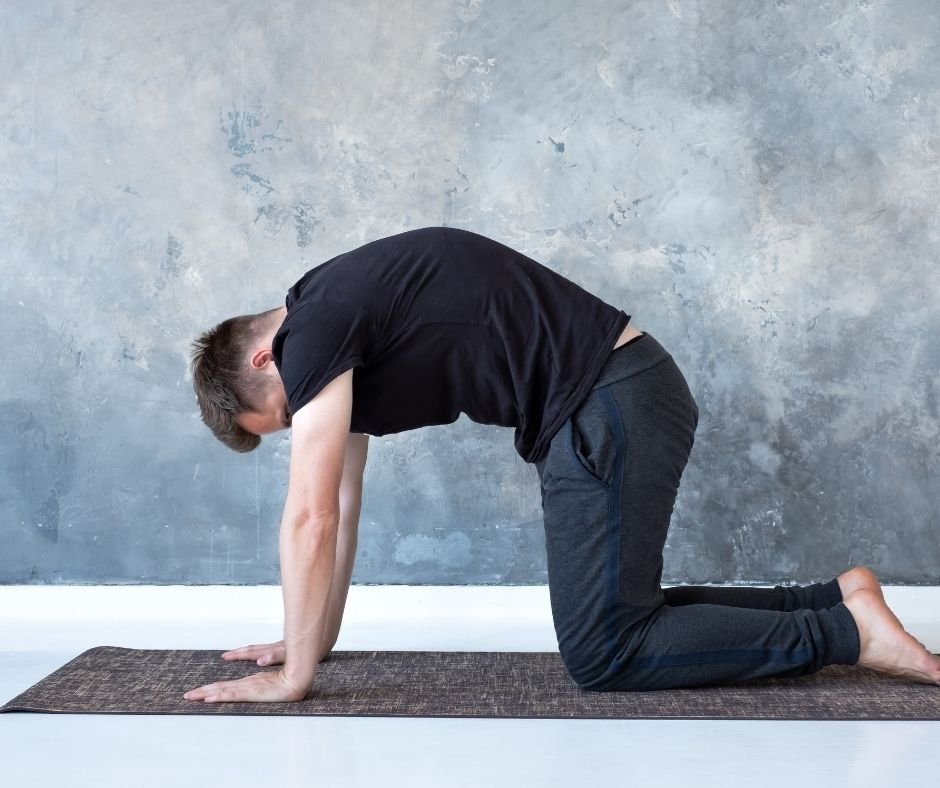
Number one - Thread the Needle
HOW: Starting position - Start in a four point kneeling with your hands and knees on the ground. Slowly rotate to one side by bringing your arm under your body and through to the other side. To increase the stretch, you can “crawl your fingers” and exhale at the end of the stretch.
FEEL: You should feel a nice and stretch in the middle region of your back when you perform this exercise.
WATCH POINTS: Make sure to keep your hips over the top of your knees, or even sink your hips back more towards your ankles.
Number two - Foam Roller Thoracic Spine Extensions.
HOW: Starting position - Place the foam roller across your thoracic spine, at your shoulder blades. Place your hands behind your head, and gently extend over the roller
FEEL: You should feel a gentle stretch through your thoracic spine, between your shoulder blades.
WATCH POINTS: Make sure to keep your bottom on the floor! Avoid hinging at the lumbar spine.
Number three - Foam Roller Pec Stretch
HOW: Starting position - Start by lying on The Foam roller with your bottom on one end, and your head on the other. Bring your arms out to 90 degrees, with your elbows bent. Relax and let your arms stretch towards the floor.
FEEL: You should feel a nice gentle stretch through the front of your shoulders.
WATCH POINTS: You should not feel pain in your shoulders. if this is the case, modify your arm position to find a pain-free stretch.
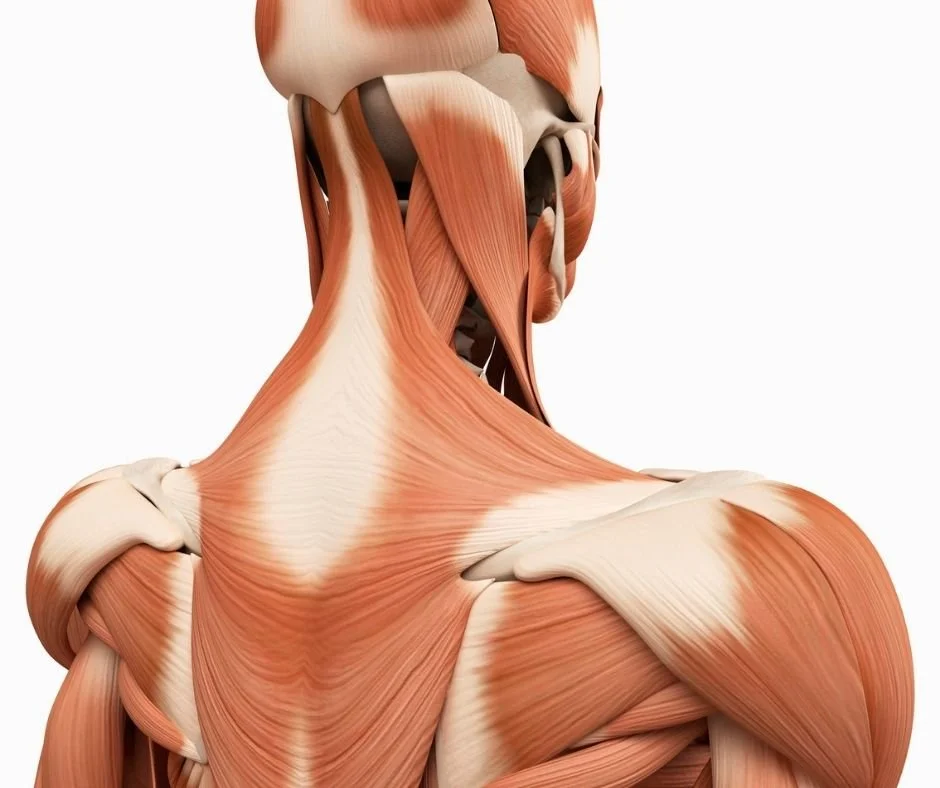
Anatomy of upper back muscles
The thoracic spine is made up of a complex network of muscles, tendons, and ligaments. These muscles are responsible for holding the shoulder blades in place and allowing the arms to move freely. The largest muscle in the thoracic spine is the trapezius, which extends from the base of the neck to the middle of the shoulder blade. This muscle is responsible for stabilizing the shoulder blades and drawing them together, is made up of the lower, middle and upper traps.
The latissimus dorsi is another large muscle that runs from the lower back to the top of the shoulder blade. This muscle is responsible for drawing the shoulder blade down and back. Together, these two muscles provide a great deal of strength and stability to the thoracic spine.
The Rhomboids - stretching the rhomboids is important in order to maintain good posture and prevent pain in the thoracic spine and shoulders. The rhomboids are a group of muscles that run from the inside edge of the shoulder blade to the spine. These muscles are responsible for drawing the shoulder blades together and keeping them stabilized.
The levator scapulae is a muscle that runs from the base of the skull to the top of the shoulder blade. This muscle is responsible for elevating (lifting) the shoulder blade. stretching the levator scapulae is important in order to prevent pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulders.
The erector spinae is important in order to maintain good posture and prevent pain in the lower back. The erector spinae is a group of muscles that runs from the base of the skull to the tailbone. These muscles are responsible for stabilizing the spine and keeping it upright.
Strengthening exercises for the upper back muscles
Upper back pain is a common problem, especially for people who sit at desks all day. The upper back muscles play an important role in supporting the spine, and when they are weak, it can lead to pain and discomfort.
If you're looking to strengthen your thoracic spine, there are a few exercises you can try. One is the "Superman" stretch, which involves lying face down on the ground and stretching your arms out in front of you. Another is the "Seated Crucifix", which entails sitting with your legs crossed and reaching your arms up overhead. Additionally, you can try the "Reverse Fly", which requires you to hold a weight in each hand and lift your arms out to the side. By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you can help to build strong upper back muscles.
Other ways to manage thoracic spine and neck pain
Thoracic spine and neck pain can be a real nuisance. It can make it hard to sit for long periods of time, and it can even make it difficult to get a good night's sleep. There are a few things that you can do to help manage upper back pain.
First, try to maintain good posture. This means sitting up straight and avoiding slouching.
Second, take breaks throughout the day to move around and stretch your back muscles.
Third, consider using an ergonomic chair or back support cushion when sitting for long periods of time.
Finally, if your upper back pain is severe, you may want to consult with a physical therapist to find out what other treatment options are available.
Why is stretching and strengthening the upper back muscles so important?
For many of us, upper back pain is a familiar feeling. Whether it's from hunching over a computer all day or from carrying around a heavy backpack, back pain is a common complaint. And while there are a variety of ways to treat back pain, one of the most effective is to stretch and strengthen the muscles in the thoracic spine. By increasing the flexibility and strength of the upper back muscles, you can help to prevent or reduce upper back pain. In addition, stretching and strengthening the upper back muscles can also improve your posture and alleviate tension headaches. So if you're looking for a way to reduce upper back pain, stretching and strengthening your upper back muscles is a great place to start.
How to prevent a hunchback posture
Most of us spend our days hunched over computers or phones, and as a result, we often suffer from back pain. Stretching and strengthening the muscles in this area can help to alleviate pain and improve posture. By maintaining a healthy thoracic spine, we can also reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions such as arthritis. Additionally, strong upper back muscles help to support the neck and prevent injuries. For all these reasons, it is essential to stretch and strengthen the thoracic spine on a regular basis. By doing so, we can enjoy improved health and a better quality of life.
Breathing and upper back pain
upper back pain can be a real pain in the neck...literally! upper back pain is a common problem that can be caused by a variety of things, including poor posture, muscle tension, and repetitive strain injuries. While there are many different treatments for upper back pain, one simple and effective remedy is to focus on your breathing.
Most of us breathe shallowly and unevenly, which can contribute to muscle tension and upper back pain. However, when we breathe deeply and evenly, it helps to relax the muscles and ease the pain. Additionally, deep breathing helps to improve our posture by lengthening the spine and opening up the chest. If you're struggling with upper back pain, start by paying attention to your breath.
If you're not breathing properly, it can put a lot of strain on your upper back and lead to pain. There are a few different breathing techniques that you can try that may help reduce upper back pain. One is diaphragmatic breathing, which is where you breathe from your stomach instead of your chest. This type of breathing can help increase the amount of oxygen in your blood and reduce upper back pain. Another breathing technique is abdominal breathing, which is where you breathe from your lower abdomen.
Final Thoughts - Upper Back Stretches
Do these upper back stretches to help improve your posture and feel better. We hope you enjoyed this post on how to stretch your upper back. Be sure to check out our other posts for more exercise tips and advice.